DIABETES
How Diabetes can Affect your Feet
Diabetes can significantly impact foot health, increasing the risk of poor circulation, nerve damage, and slow-healing wounds. Podiatric care plays a crucial role in early detection, prevention, and management to help protect your feet and overall health.
Regular foot exams, proper footwear, and daily foot care routines are essential for people with diabetes. A podiatrist can identify subtle changes before they become serious complications, helping you stay active and avoid infections, ulcers, or even amputations. Prioritizing your foot health is a vital part of managing diabetes and maintaining your quality of life. Consistent care and attention can prevent small issues from becoming major health risks over time.
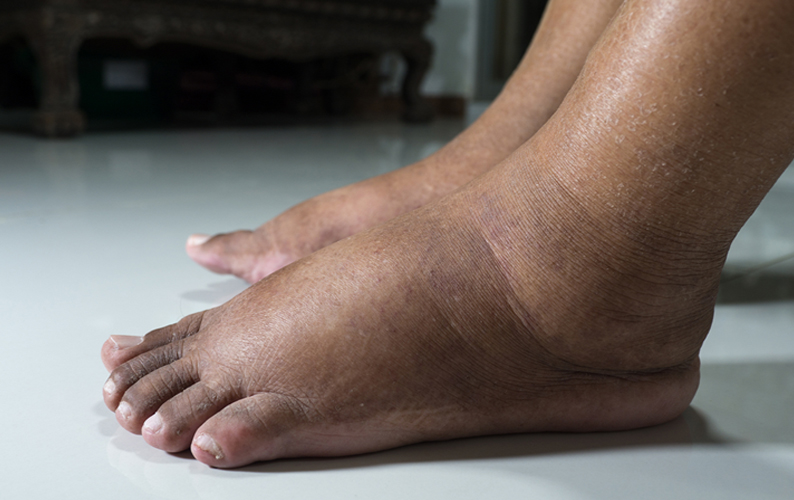
Today’s podiatrist plays a key role in helping patients manage diabetes successfully and avoid foot-related complications.
Diabetic Wound Care
A diabetic foot ulcer is an open sore or wound that occurs in approximately 15 percent of patients with diabetes and is commonly located on the bottom of the foot.
High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure is also known as hypertension. Your podiatrist is vitally concerned about hypertension and vascular disease (heart and circulatory problems).
Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD)
PAD is caused by a blockage or narrowing of the arteries in the legs when fatty deposits (plaque) build-up. The buildup of plaque causes the arteries to harden and narrow.
Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy is damage to the peripheral nerves—the nerves in your toes and fingertips. In the United States, the most common cause of peripheral neuropathy is diabetes.